Guidelines for PFAS Waste Management at Industrial Sites
Guidelines for PFAS Waste Management at Industrial Sites
Blog Article
Innovative PFAS Treatment Solutions for Safer Water
The increasing occurrence of PFAS contamination in water products demands a crucial exam of cutting-edge treatment solutions. Advanced filtering technologies and unique chemical treatments present promising methods for decreasing these relentless pollutants. Furthermore, emerging bioremediation strategies offer an even more lasting strategy to taking on PFAS challenges. As regulatory frameworks proceed to adapt, recognizing the performance and scalability of these options comes to be critical. What ramifications do these innovations hold for public health and environmental reconstruction, and how can stakeholders properly execute them in diverse contexts?
Introduction of PFAS Contamination
PFAS contamination has actually emerged as a significant environmental and public health problem. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) are a group of synthetic chemicals recognized for their perseverance in the setting and body, leading them to be typically referred to as "for life chemicals." These compounds have actually been commonly used in different industries, consisting of firefighting foams, water-repellent fabrics, and food product packaging, mainly because of their water- and grease-resistant residential properties.
The extensive use PFAS has actually led to their detection in soil, water materials, and even in the blood of human beings and pets. Research studies have actually linked PFAS direct exposure to countless health problems, including developmental impacts in infants, body immune system dysfunction, and various forms of cancer cells. Furthermore, the ecological perseverance of these compounds complicates their destruction and elimination, raising issues concerning lasting environmental influences.
Regulatory bodies are increasingly carrying out strict standards to check and reduce PFAS degrees in drinking water and other ecological mediums. As awareness of PFAS contamination expands, it has become important for communities and markets to seek effective treatment services to minimize exposure and protect public wellness.
Advanced Filtering Technologies
As the necessity to attend to PFAS contamination intensifies, progressed filtration modern technologies have actually become a critical component in the removal initiatives focused on eliminating these persistent chemicals from water sources. These modern technologies leverage advanced mechanisms to properly target and capture PFAS substances, which are notoriously immune to traditional therapy approaches.
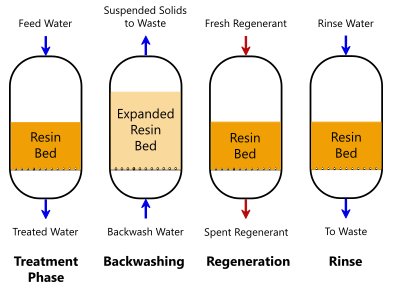
One of one of the most promising strategies is making use of granular triggered carbon (GAC), which adsorbs PFAS molecules because of its high surface and permeable framework. This approach has actually been extensively applied in both municipal and commercial settings, demonstrating substantial reductions in PFAS focus. Furthermore, ion exchange materials have actually gotten grip, especially developed to uniquely bind PFAS ions from water, hence promoting their elimination.
Membrane purification technologies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, also reveal efficiency in PFAS removal by literally separating contaminants from water - pfas management. These systems can attain high degrees of pureness, making them ideal for alcohol consumption water applications
Chemical Treatment Developments
Many chemical therapy innovations are being explored to effectively attend to PFAS contamination in water materials. One encouraging technique includes making use of innovative oxidation procedures (AOPs), which utilize effective oxidants such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or chlorine dioxide combined with UV light to damage down PFAS compounds into less damaging substances. This technique has actually demonstrated effectiveness in research laboratory setups, revealing prospective for scalability in real-world applications.
Another innovative method is the growth of ion-exchange materials specifically created to target PFAS. These resins can precisely adsorb PFAS substances from water, permitting for their removal during therapy procedures. Current developments have boosted the performance and ability of these resins, making them a beneficial option for water therapy facilities.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the use of chemical representatives like persulfate and ferrous ions to improve the degradation of PFAS in infected water. These agents can induce chemical reactions check my site that assist in the malfunction of relentless PFAS substances.
Arising Bioremediation Strategies
Recent advancements in chemical treatment developments have led the way for discovering bioremediation strategies as a sensible alternative for addressing PFAS contamination. Bioremediation harnesses the all-natural metabolic processes of microorganisms to degrade or change contaminants, making it an enticing strategy for taking on relentless pollutants like PFAS.
Arising methods in bioremediation consist of making use of genetically crafted bacteria that can particularly target and break down PFAS compounds. These microbial pressures are being created for their boosted destruction capacities, boosting the effectiveness of the remediation process. In addition, scientists are examining the possibility of plant-assisted bioremediation, where certain plant species might uptake and sequester PFAS from contaminated soil and water.
Another appealing method is the application of bioaugmentation, which includes presenting beneficial bacteria into infected settings to improve the degradation of PFAS. This technique can help with quicker remediation timelines and enhance total performance.

Regulatory Structures and Criteria
An extensive regulative structure is important for successfully taking care of PFAS contamination and making certain public health and wellness great post to read protection. The increasing acknowledgment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as environmental toxins has actually motivated numerous government and state companies to develop requirements that regulate their visibility in water supplies. The United State Environmental Defense Firm (EPA) has developed health and wellness advisories and is pursuing establishing enforceable limits for PFAS in alcohol consumption water.
State-level guidelines vary significantly, with some states adopting more stringent standards than those suggested by the EPA. These regulations typically consist of maximum impurity degrees (MCLs) for particular PFAS substances, monitoring demands, and reporting commitments for water utilities. Furthermore, emerging structures concentrate on the remediation click site of infected websites, stressing the requirement for efficient therapy modern technologies.
Final Thought
To conclude, the growth and implementation of ingenious PFAS treatment options are crucial for attending to the pervasive concern of water contamination. Advanced purification technologies, chemical therapies, and arising bioremediation strategies jointly present a multifaceted method to properly minimize and deteriorate PFAS levels. As regulative structures remain to develop, integrating these modern technologies will be essential to safeguard public wellness and recover the stability of contaminated water sources, eventually adding to a cleaner and more secure setting.
Report this page